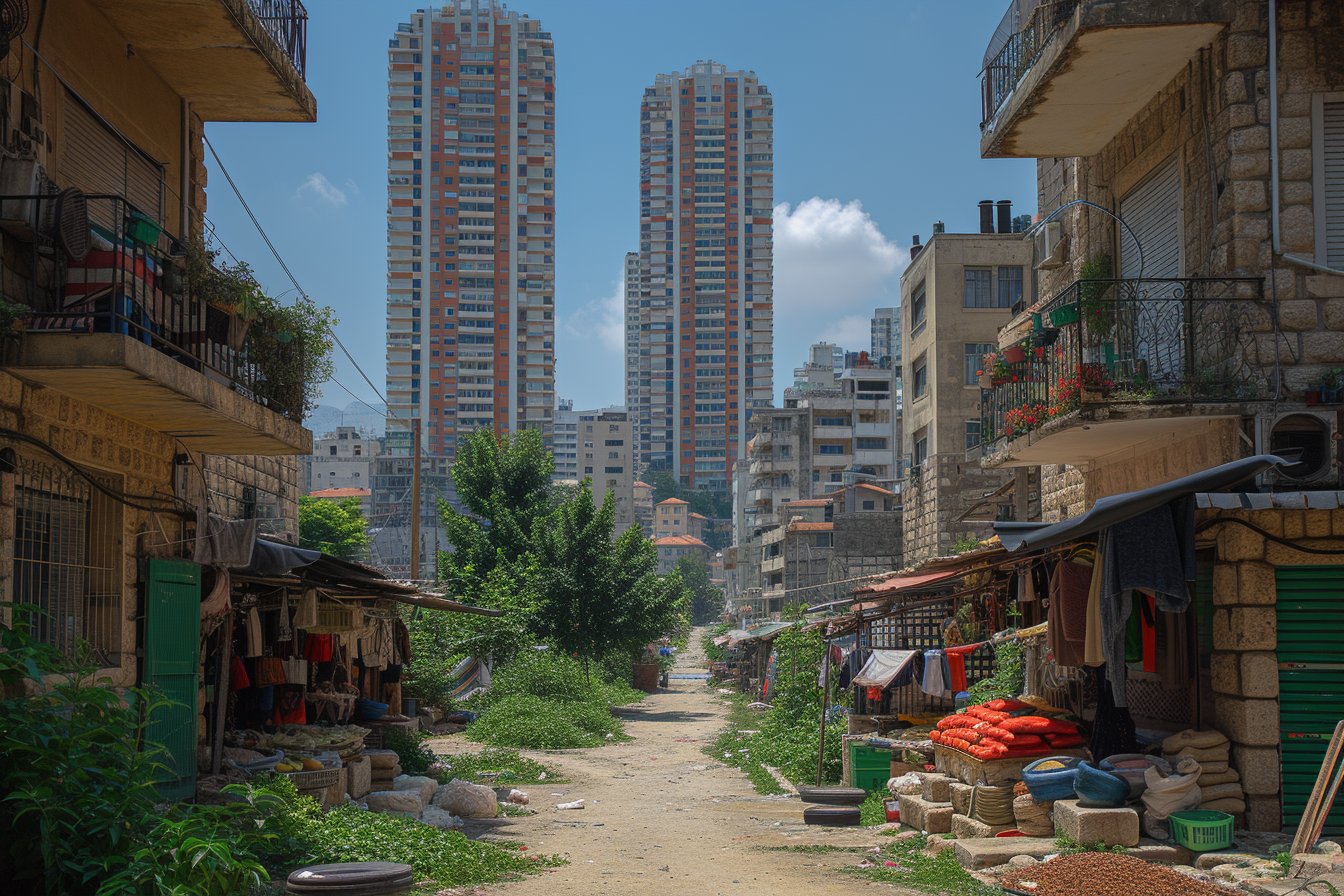
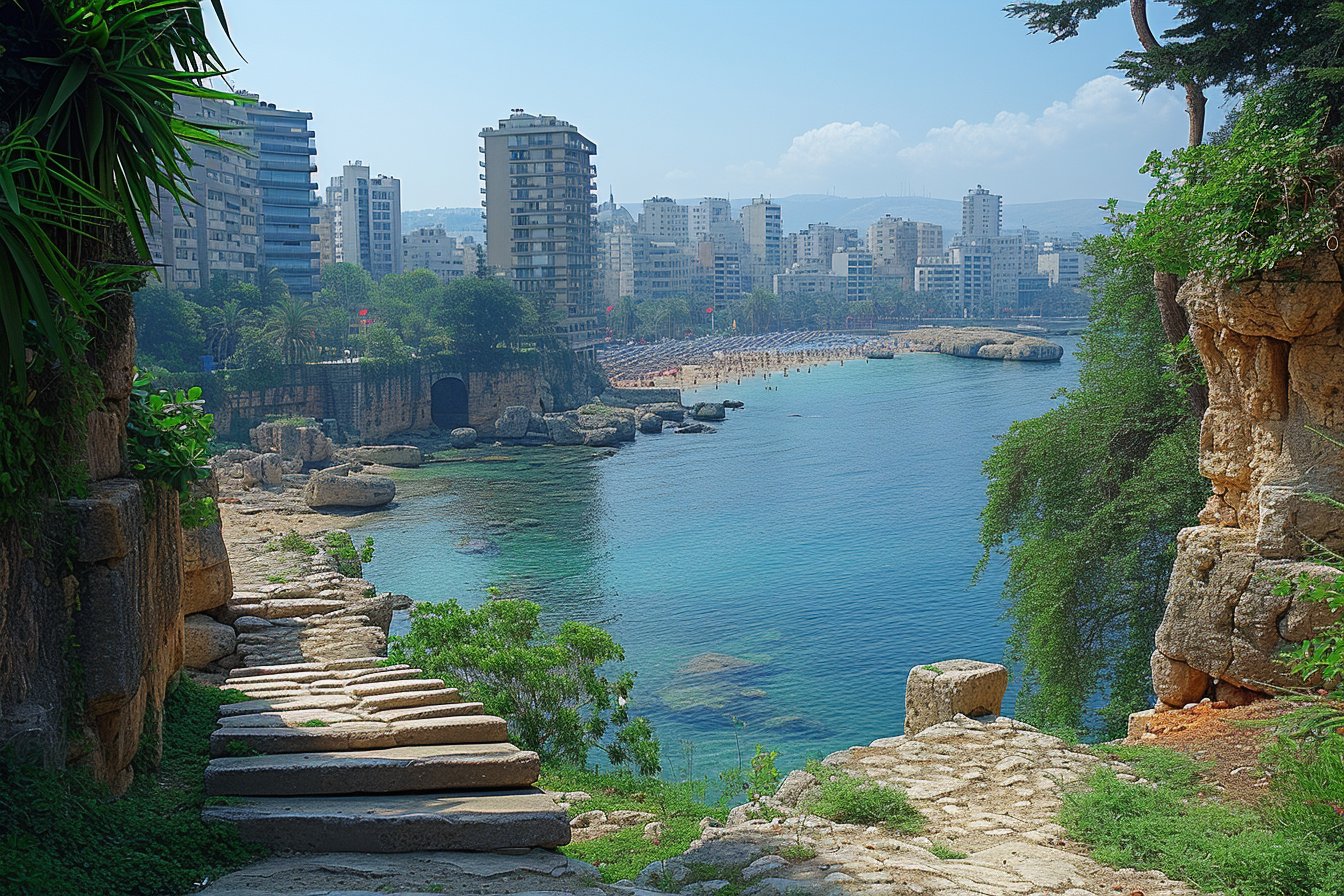
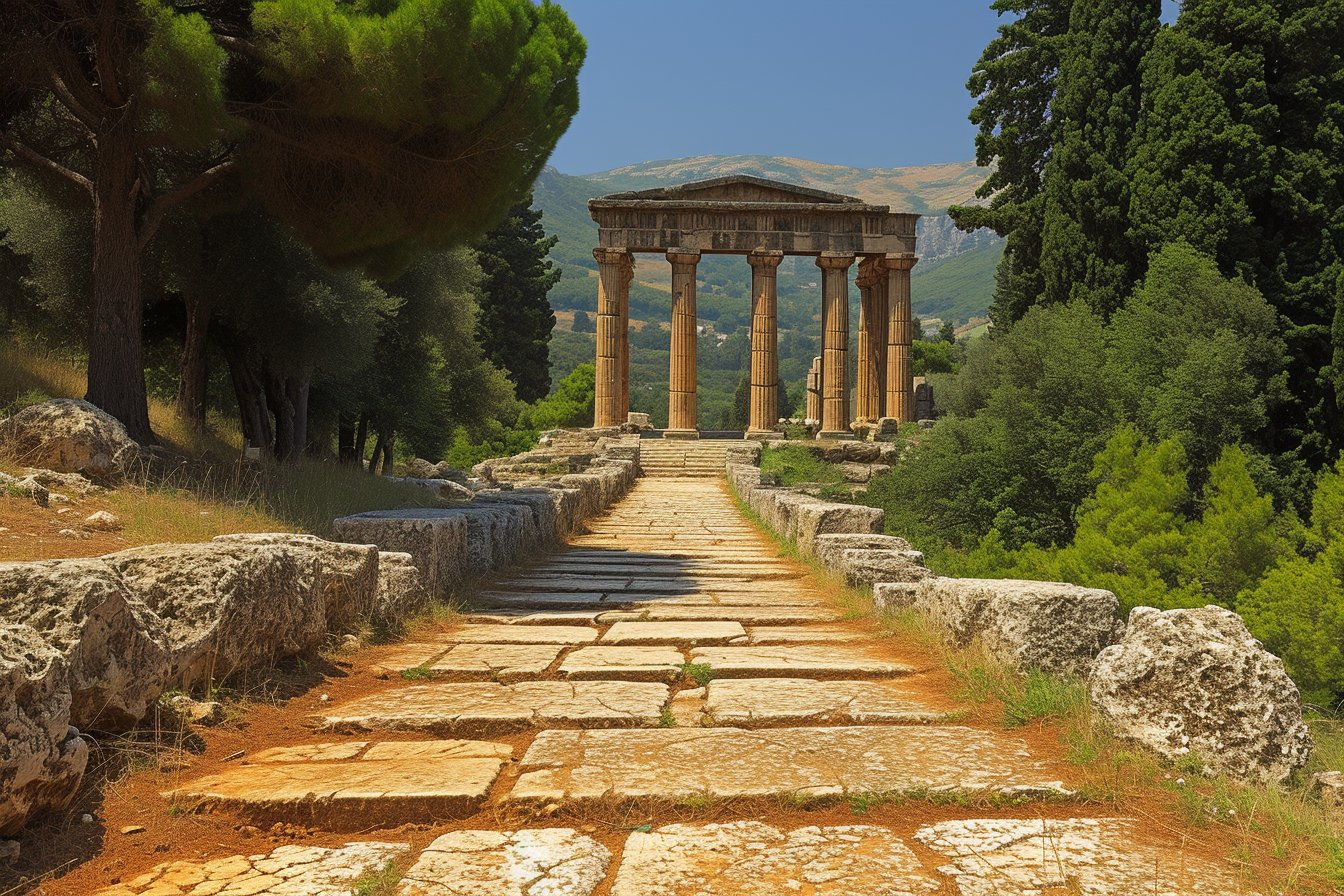
In the history of its existence, Lebanon has faced numerous challenges and conflicts that have shaped its current state of peace. The country, nestled in an area surrounded by decades of unrest, has struggled to maintain a sense of harmony among its diverse religious and cultural groups.
A Brief Overview of Lebanon’s Past
Located on the Eastern Mediterranean Coast, Lebanon shares its borders with Syria to the north and east, as well as Israel to the south. This prime location has not only made it susceptible to external threats but also contributed to political strife within its boundaries. With a rich history dating back thousands of years, different empires and dynasties have ruled Lebanon at various points in time. However, since gaining independence in 1943, Lebanon has been working tirelessly to establish peaceful existence despite the tumultuous regional environment.
Impact of Neighboring Conflicts
The longstanding tensions between neighboring countries such as Israel and Syria have undoubtedly influenced Lebanon’s political landscape. For instance, the Israeli-Lebanese conflict dates back to 1948, when the establishment of the State of Israel put the two nations at odds. Multiple clashes occurred, leading to the Israeli invasion in 1982 and subsequent occupation of Southern Lebanon until 2000.
Similarly, the Syrian civil war has had a profound impact on Lebanon’s stability. Since the beginning of the protests against the Syrian government in 2011, both refugees and militants have crossed into Lebanon, further fueling sectarian tensions within the country.
Internal Conflict Complications
Perhaps one of the most defining internal conflicts in Lebanon’s recent history is the Lebanese Civil War, which took place from 1975 to 1990. It was caused primarily by political and religious differences between the various factions residing in the country. The war resulted in an estimated 120,000 fatalities, as well as widespread destruction and a long-lasting impact on Lebanon’s road to peace. As with past conflicts, the end of the civil war did not signify a complete restoration of peace but rather opened doors for further tensions to arise.
Lebanon’s Strive for Harmonious Coexistence
The primary focus for achieving peace within Lebanon is centered around fostering harmonious coexistence among its diverse religious, political, and ethnic groups. The Lebanese constitution ensures equal rights for all citizens regardless of their religious affiliations and promotes power-sharing to maintain balance.
The Political System: Sectarian-based Power Sharing
To ensure fair representation for each sect in the government, positions are allocated based on religious affiliation. This so-called confessional system, which includes the President (a Maronite Christian), the Prime Minister (a Sunni Muslim), and the Speaker of Parliament (a Shia Muslim), aims to achieve equality on the political front.
However, the sectarian nature of politics concurrently breeds division and tends to influence policies, either directly or indirectly, based on religious affiliations – highlighting the complexity of balancing diversity with unity.
Social and Cultural Integration Efforts
In addition to the governmental approach, efforts to encourage inclusivity exist in the Lebanese society at large. A large portion of the population supports secularism and wants to foster an environment where individuals are considered Lebanese citizens first and foremost, without labeling them according to their religious or political affiliations.
Furthermore, cultural events like music festivals and exhibitions that showcase the plurality inherent in Lebanon provide a space for shared experiences and mutual understanding, effectively working to transcend political and religious divides.
Challenges Faced in Pursuit of Peace
The path toward complete peace within Lebanon remains riddled with numerous obstacles. Some of the most significant challenges faced by the nation today include:
- Economic Crisis: The Lebanese economy has been struggling under high levels of debt, inflation, and unemployment, further exacerbated by the ongoing pandemic. This financial hardship feeds into social unrest and threatens stability.
- Refugee Influx: Since the onset of the Syrian civil war in 2011, Lebanon has taken in a substantial number of refugees, drastically impacting its infrastructure and resources – adding immense pressure on an already strained system.
- External Influence: Tensions surrounding Iran’s growing influence in the region may contribute to worsening the situation in Lebanon. The proxy conflicts involving Iran-backed Hezbollah militias could cause further friction between Lebanese factions and undermine any chance for lasting peace.
In Conclusion: A Priceless Goal Unperceived
Lebanon is a country that grapples with social, economic, and political complexities, both internal and external. Its endeavors to maintain peace through power-sharing and cultural integration have provided mixed results – reflecting both the strengths and limitations inherent within these approaches.
With continued efforts and collaboration among different factions and sectors of society, Lebanon can strengthen its pursuit of unity and work towards achieving lasting peace – a goal priceless and unperceived, yet indispensable to its identity and future.