In order to examine the financial status of Lebanon, it is essential to have a comprehensive understanding of its economy, demographics, and sources of income. To answer the question, “Is Lebanon a rich or a poor country?”, this article will explore different indicators that define its wealth and poverty situation.
A Brief Overview of Lebanon’s Economy
Lebanon is a small Middle Eastern country with a population of around 6.8 million people living within an area of just over 10,000 square kilometers. The nation has a diverse economic system comprising services, tourism, and agriculture sectors. Despite being blessed with beautiful landscapes and historical sites that attract millions of tourists every year, Lebanon faces various challenges such as political instability, high unemployment, rising inflation, and increasing public debt.
The Gini Coefficient: A Measure of Income Inequality
One method for determining the disparity between rich and poor within a country is through the Gini coefficient, which ranges from 0 (perfect equality) to 1 (maximum inequality). According to World Bank data from 2019, Lebanon’s Gini coefficient stands at 0.33, placing it among the countries with moderate income inequality levels. This suggests that while the gap between the rich and poor in Lebanon is significant, it is not as pronounced as some other nations.
Poverty Levels in Lebanon
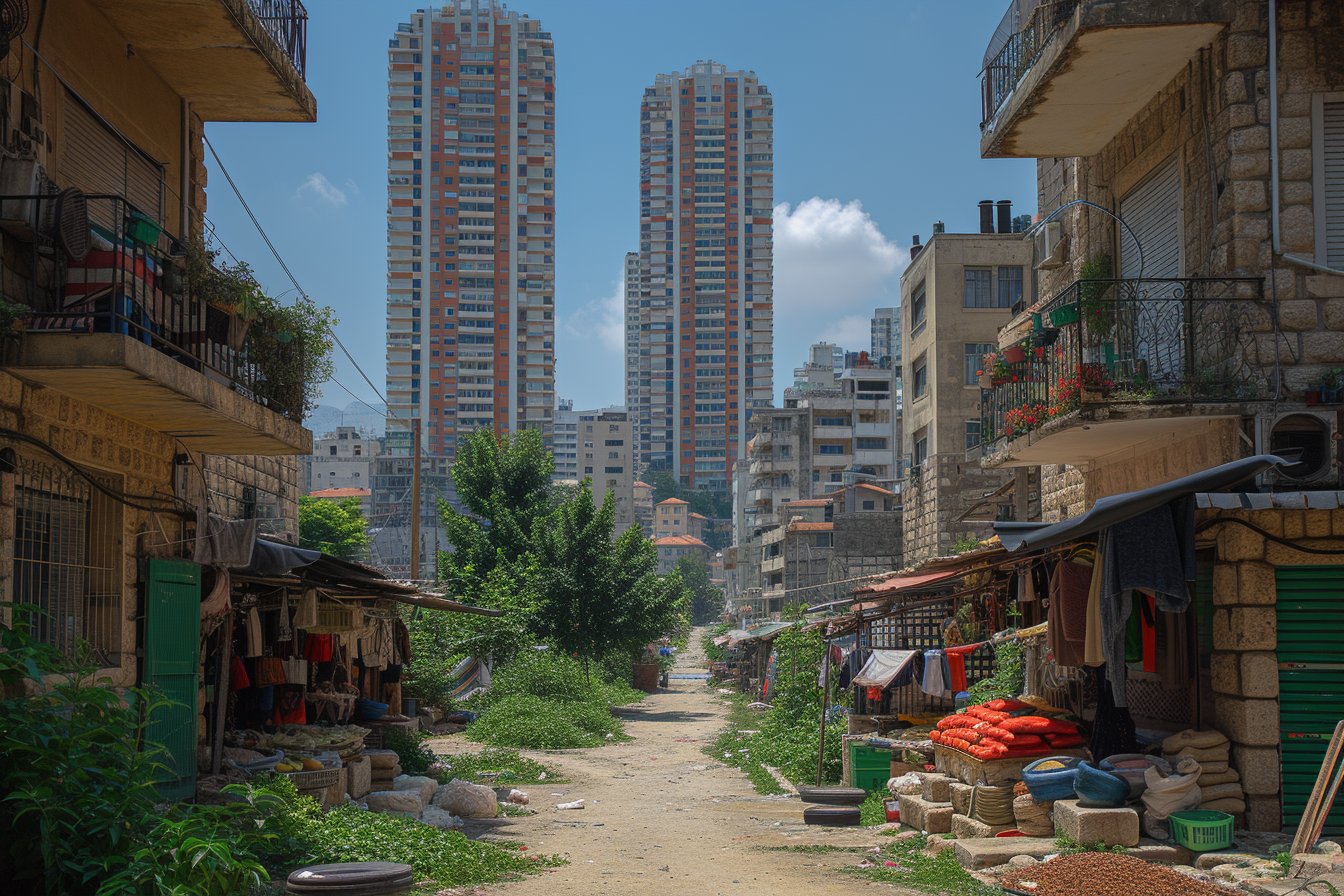
Although there are many affluent areas and wealthy individuals residing within Lebanon, there remains a substantial proportion of the population experiencing poverty. Based on recent reports, more than half of the residents live under the poverty line.
Unemployment Rate
An essential determinant of poverty is the unemployment rate, defined as the percentage of jobless people in a country’s total population. Lebanon experiences high unemployment levels, particularly among youth and recent university graduates. According to International Labour Organization (ILO) data from 2020, Lebanon has an overall unemployment rate of approximately 11%. However, the unemployment rate for young adults is even higher at over 20%.
Impacts of the Syrian Refugee Crisis
The ongoing Syrian refugee crisis has significantly impacted the poverty situation in Lebanon. With over one million registered Syrian refugees residing within its borders, this influx of migrants has strained Lebanon’s infrastructure, increased competition for scarce jobs, and driven down wages for low-skilled workers. The United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees (UNHCR) estimated that around 70% of these refugees live below the poverty line, further exacerbating the nation’s financial struggles.
Sources of Wealth in Lebanon
Despite its challenges with poverty, Lebanon does possess various sources of wealth and income, as evidenced by the presence of prosperous industries and affluent citizens. Let’s explore some of the significant contributors to Lebanon’s economy.
Banking Sector
Lebanon boasts a strong banking system with nearly 200 banks operating within the small nation. The country’s Central Bank, Banque du Liban, has played a critical role in maintaining monetary stability amidst political turmoil and economic shocks throughout the years. Moreover, Lebanese expatriates working abroad continue to contribute billions of dollars annually to the domestic banking sector through remittances.
Tourism and Hospitality Industry
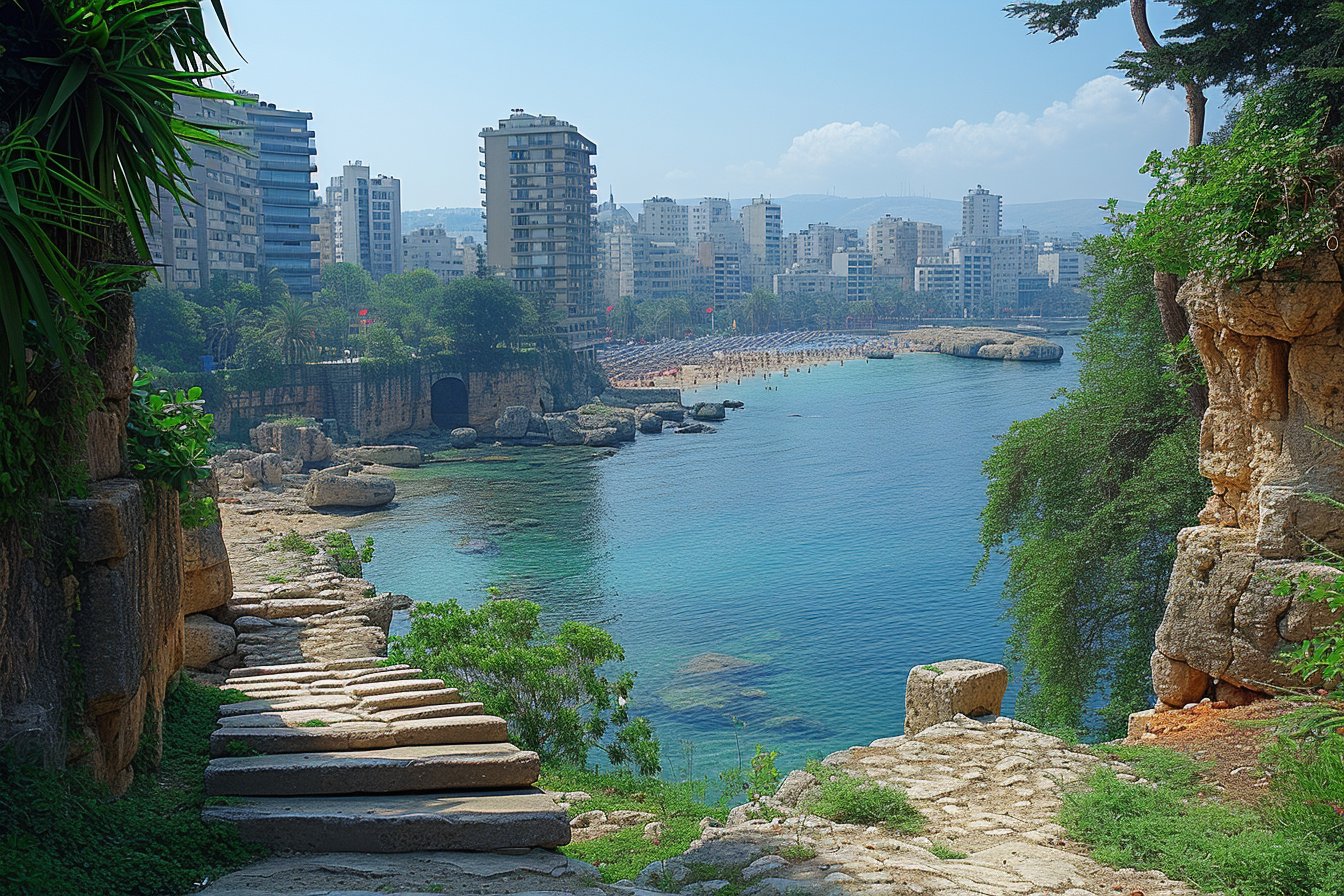
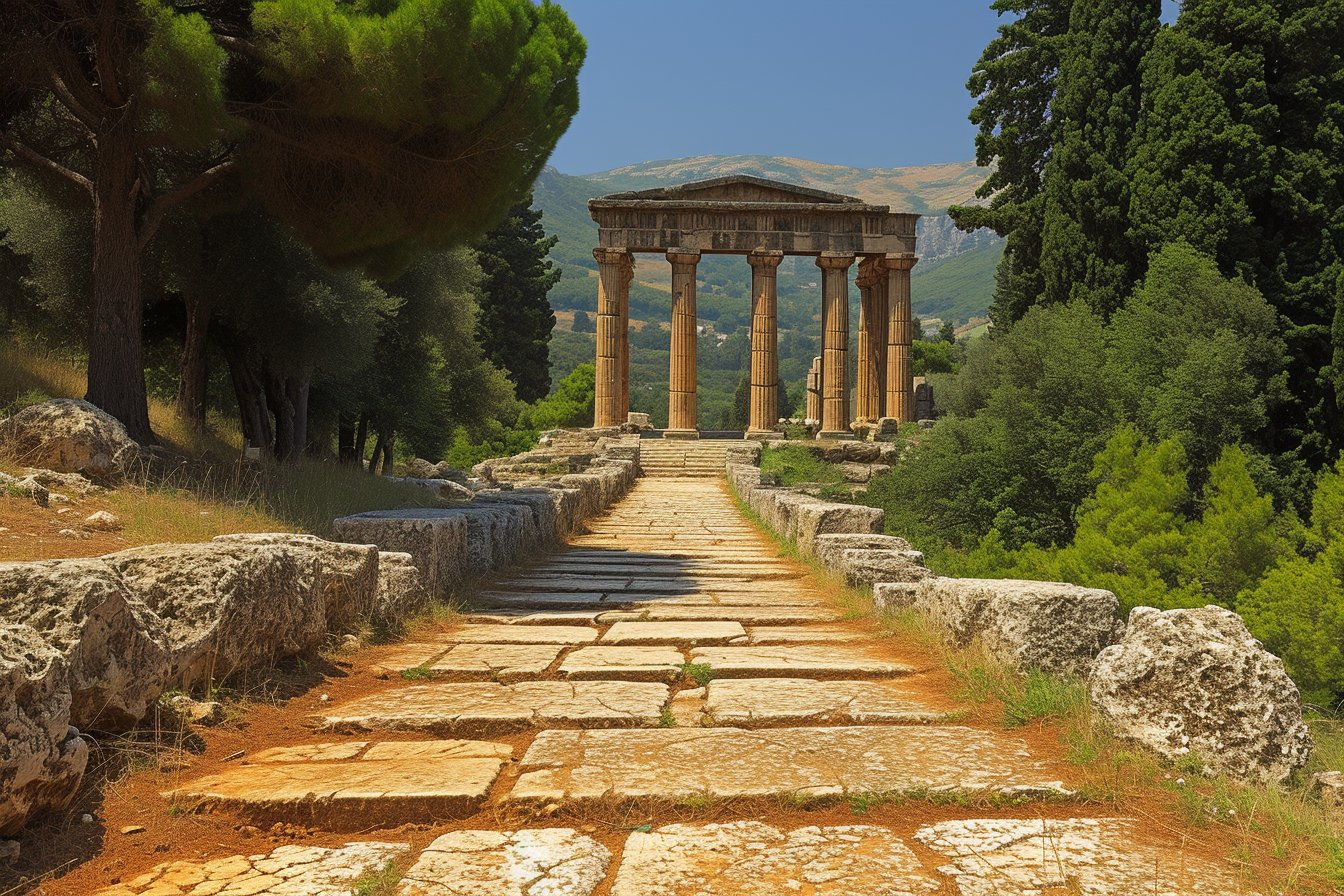
Lebanon’s picturesque landscapes, rich history, and warm hospitality make it an appealing destination for tourists worldwide. With countless historical sites, such as the ancient Roman ruins in Baalbek and the Jeita Grotto – one of the world’s most impressive cave systems, the country continues to attract millions of visitors annually. Consequently, tourism and hospitality sectors have served as essential sources of income for Lebanon.
Agriculture
Lebanon’s fertile lands allow for thriving agricultural production. Agricultural sectors contribute approximately 3% of the nation’s GDP, providing employment opportunities for many rural families. Renowned regional products include olives, tobacco, fruit, and grapes used in the nation’s growing wine industry.
Poverty Alleviation Efforts by Organizations and Government Programs
In light of poverty challenges facing the population, various organizations and government programs aim to support vulnerable communities throughout Lebanon. Some key initiatives include:
- National Poverty Targeting Program (NPTP): This program provides social assistance, including financial aid, food packages, and health coverage, to underprivileged Lebanese families identified through a rigorous selection process.
- Rental Subsidy Cash Assistance Program: Implemented with UNHCR support, this program assists vulnerable refugees with rental subsidies to ensure access to safe and affordable housing.
- Education and Skills Training Programs: Numerous NGOs operate within Lebanon, focusing on providing education and vocational training for youth to enable them to earn a sustainable living and break the cycle of poverty.
By addressing critical areas such as access to basic needs, healthcare, education, and employment, these efforts hope to alleviate some of the struggles faced by impoverished citizens in Lebanon.
In summary, determining whether Lebanon is a rich or poor country entails a multifaceted approach that considers factors such as income inequality, poverty rates, sources of wealth, and efforts towards poverty alleviation. Recognizing that Lebanon possesses both extreme wealth and widespread poverty, it is crucial to seek out sustainable solutions that aim at closing the income gap, providing opportunities to disadvantaged individuals, and fostering long-term economic growth for Lebanon as a nation.